Last Updated August 15, 2024
The Ultimate SEO Audit Checklist to Boost Your Website
There are many websites competing for attention, and only those that follow search engine guidelines will be successful. Performing a complete SEO audit is crucial because it directly impacts how easily people can find your website online, which can directly influence your online presence and, consequently, contribute to the growth of your business.
You’ll learn what you need to know before starting an SEO audit. This includes knowing your destination by setting your goals, how your website is currently performing, and checking your competition to look for gaps and opportunities.
This article will also explain the different aspects of an SEO audit, including technical aspects, improving your website’s content, and tracking your progress.
Why SEO audit is important for your website
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) audit is a comprehensive analysis of your website’s congruence with the best practices in the digital marketing world. It is the first step in formulating an implementation plan that will have measurable results. The audit aims to identify foundational issues affecting organic search performance.
The benefits and importance of conducting an SEO audit include:
- Improving Site Health: Just like regular health check-ups, an SEO audit can detect common issues, such as broken links and duplicate content, that may affect your site’s performance.
- Enhancing User Experience: It ensures the website is user-friendly, has a responsive design, and has responsive design quick load times to reduce bounce rate
- Increased Visibility: By optimising technical SEO issues, your site’s visibility to search engines is improved, thereby increasing organic traffic.
- Staying Updated: The audit helps you stay current with the latest search engine algorithms and adjust your strategy accordingly.
- Competitive Analysis: An SEO audit distinguishes you from competitors by highlighting opportunities to outperform them in search ranking
An SEO audit is not a one-time task but an ongoing process that keeps your website healthy and competitive in the dynamic realm of search engines.
Preparing for the SEO audit
Ensure that you have a systematic approach to follow your SEO audit checklist and keep records of the findings for a before-and-after comparison. Proper preparation will streamline the process and make the audit more effective, allowing for a clear analysis of your website’s SEO health.
Setting clear goals and objectives
Screaming Frog is another tool that has the ability to crawl your website to look for searchability errors that might hurt your SEO.
Setting clear goals acts as your compass, guiding your audit towards the aspects that will have the most significant impact on achieving your desired outcomes.
For instance, if your goal is to increase organic traffic for e-commerce conversions, your audit will prioritise optimising product pages, improving internal link structure, and ensuring mobile-friendliness.
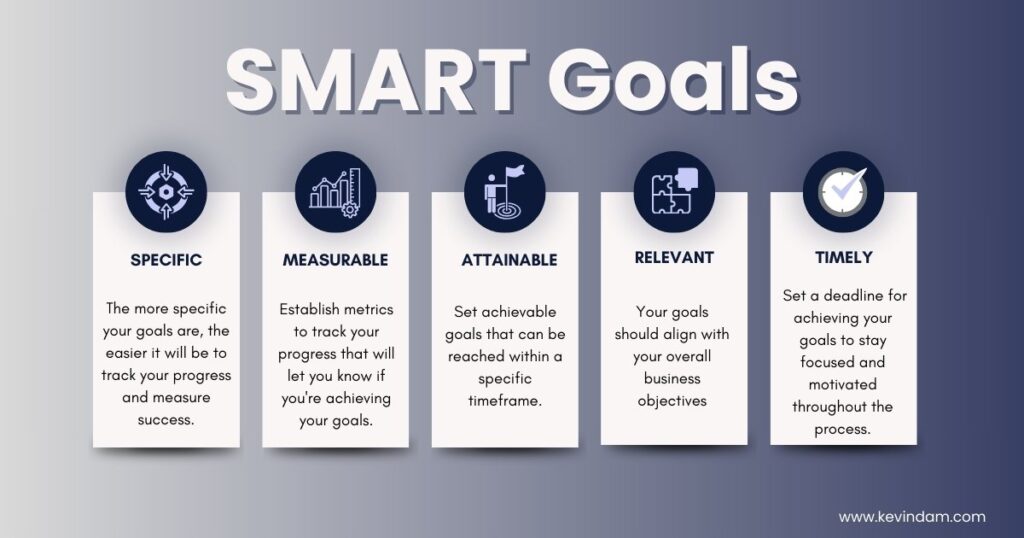
Here’s the SMART framework to set effective goals:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve. Do you want to increase organic traffic by 20%? Improve your ranking for specific keywords related to your products or services. The more specific your goals are, the easier it will be to track your progress and measure success.
- Measurable: Establish metrics to track your progress. Your metrics will let you know if you’re achieving your goals. Set quantifiable targets for each goal. For example, if you want to increase organic traffic by 20%, you’ll need to track your website’s monthly organic traffic using Google Analytic
- Attainable: Be realistic about what you can accomplish. Set achievable goals that can be reached within a specific timeframe. Website’s current performance, industry competitiveness, and resource availability are some factors you can consider.
- Relevant: Your goals should align with your overall business objective How will improving SEO benefit your website and your business? You may want to increase brand awareness, generate more leads, or boost online sales.
- Timely: Set a deadline for achieving your goals. This will help you stay focused and motivated throughout the SEO audit Having a specific timeframe will also allow you to make adjustments to your strategy if needed.
Setting these objectives beforehand will not only direct your efforts but also give you a benchmark to measure your success.
Reviewing your website’s current performance metrics
To fully grasp the scope of work required during your SEO audit, you need to review your website’s current performance metrics. Utilise tools like:
- Google PageSpeed Insights to check for loading times
- Google Analytics to analyse organic traffic patterns
- Google Search Console to uncover technical SEO issue
- your site’s Core Web Vitals to understand user experience elements like loading, interactivity, and visual stability.
This review will create a performance baseline and help you identify the most pressing areas needing improvement.
Analysing your target audience and competitors
Understanding your target audience and analyzing your competitors are key components of an effective SEO audit. Determine who your audience is, what they are searching for, and how they use search engines to find content.
Use this insight to refine your target keywords and content strategy. In parallel, perform a competitor analysis to identify which keywords they are ranking for, the quality of their backlinks, and their website structure. This analysis can offer strategic insights into their strengths and possible gaps you can capitalise on in your SEO strategy.
Technical SEO audit
A comprehensive Technical SEO audit is essential for identifying the underlying problems that could hamper your website’s search engine performance. This process involves closely examining your site’s architecture, evaluating your site’s adherence to best practices, and identifying any technical shortcomings that might affect its rankings.
Checking for broken links and fixing them
Fixing broken links not only aids in improving your site’s usability but also helps preserve link juice, which can be lost through dead-end links.
Finding Broken Links
- Web-based SEO Audit Tools: These are comprehensive tools that crawl your site and identify broken link Popular options include Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Sitechecker.
- Google Search Console (GSC): This free tool by Google helps you monitor your site’s health in search results. In the “Coverage” report, you can find listed URLs with errors, including “Not Found (404)”, which indicates broken link
- Screaming Frog is another tool that can help find broken internal link
To find broken internal links:
- Click the “Internal” tab
- Sort the results by “Response Codes”
- View 404, 301, or related status codes to find broken links
Once you have a list of broken links, prioritise which ones to fix first. Focus on links on high-traffic pages and those that are important to your website’s structure.
There are two main options for fixing this:
- If the target page has moved to a new location on your site, update the URL in the link.
- If the target page no longer exists, you can either remove the link or replace it with a relevant, working link.
By finding and fixing broken links, you’ll help search engines crawl your site more effectively, which can boost your SEO.
Optimising website speed using PageSpeed Insights and Core Web Vitals
Website speed is a significant factor in both user experience and SEO performance. When users encounter slow loading times, they’re more likely to abandon your site and head to a competitor’s. Search engines, particularly Google, also prioritise websites that deliver a fast and smooth browsing experience.
Here’s how Google’s PageSpeed Insights and Core Web Vitals come into play during an SEO audit to optimise website speed.
PageSpeed Insights is a free tool by Google that analyses your website’s performance on desktop and mobile devices. It provides a score (0-100) and specific recommendations for improvement. Here’s how to utilise it in your SEO audit:
- Run PageSpeed Insights for key pages on your website. Analyse the report to pinpoint areas hindering your loading speed. Common culprits include large image files, unoptimised code, and render-blocking resources.
- This tool doesn’t just highlight problems; it suggests solutions. The report provides actionable recommendations tailored to your website’s specific issues. These recommendations may include optimising images, enabling browser caching, and minifying code.
- Not all recommendations hold equal weight. PageSpeed Insights categorises suggestions as “High Impact,” “Medium Impact,” and “Low Impact.” Focus on addressing the high-impact recommendations first, as they will likely yield the most significant improvements in website speed.
Optimising for Core Web Vitals:
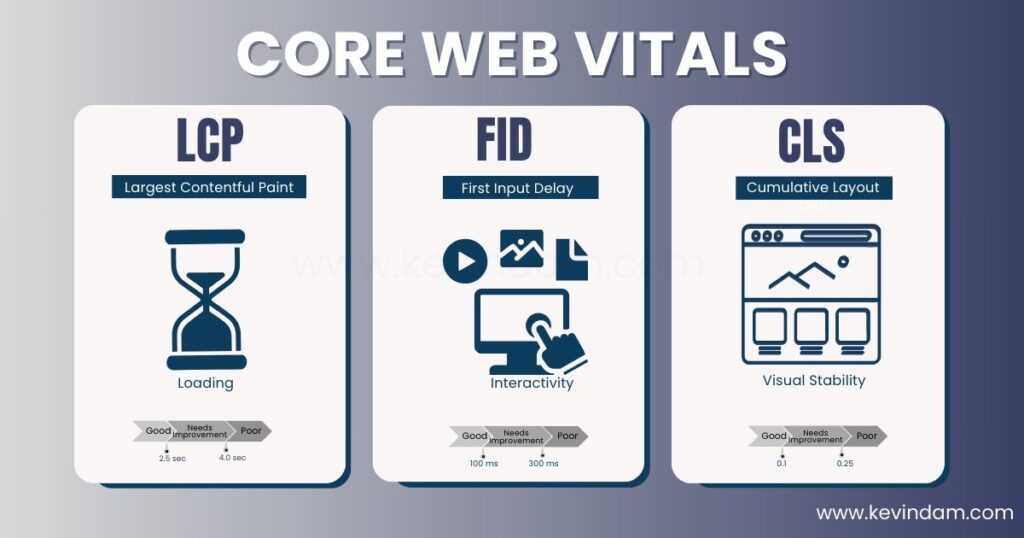
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics established by Google to measure critical aspects of user experience related to loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability. These metrics include:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures the time it takes for the main content of your page to load.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures the responsiveness of your website; how long it takes for the website to react to a user’s first interaction.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures the visual stability of your page; how often unexpected layout shifts occur while the page is loading.
Integrating Core Web Vitals into SEO Audit:
- Evaluate Current Performance: Use Google Search Console or other SEO tools to assess your website’s Core Web Vitals performance. See how your website stacks up against Google’s recommended thresholds (“Good,” “Needs Improvement,” “Poor”).
- Focus on User Experience: Prioritize improvements that directly address Core Web Vitals metrics. This ensures your website delivers a fast, interactive, and visually stable experience for users, which will, in turn, benefit your SEO ranking.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Website speed optimisation is an ongoing process. After implementing changes, re-evaluate your website’s speed. This helps you track progress and identify any new issues that may arise.
Analysing XML sitemaps
A well-structured XML sitemap is crucial for search engines to crawl and index your website effectively.
- Ensure that your sitemap is up-to-date and submitted to Google Search Console.
- Check that it includes all the pages you want search engines to discover.
- Confirm that there are no orphan pages – those not linked from other parts of your site, which can hinder a page’s visibility in the SERPs.
Advanced Analysis Tools (Optional):
- SEO tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush can crawl your site and compare it to your sitemap, highlighting discrepancies between what’s listed and what exists.
- Tools like Screaming Frog allow you to upload your sitemap and analyse the listed URLs, identifying broken links, crawl errors, and other technical issue
Proper sitemap management enables search engines to index your content more efficiently.
Site Indexing and Crawlability
Indexing and crawlability means ensuring that all the pages you want to show up in search results are actually being indexed by search engines.
Optimising Crawlability and Indexability:
- Address any crawl errors identified by your audit tools or GSC (Google Search Console). This includes fixing broken links, ensuring proper robots.txt configuration, and improving website speed.
- Screaming Frog is another tool that can crawl your website to look for searchability errors that might hurt your SEO.
- Verify that your robots.txt file isn’t unintentionally blocking important content from search engine
- Ensure your canonical tags are implemented correctly and point to the preferred version of any duplicate content.
- Review noindex tags, ensuring they are only used intentionally on pages you don’t want to be indexed.
- Focus on creating valuable and high-quality content that search engines will find worthy of indexing.
Evaluating the mobile version and responsiveness of your website
With an increasing number of users accessing the web from mobile devices, having a mobile-friendly website has become imperative for reaching a wider audience and retaining visitors. A responsive design not only caters to users across all devices but also adheres to mobile-first indexing, which can influence your search ranking.
Key Mobile SEO Audit Areas:
- Verify that your website uses responsive design and adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes and resolutions.
- Test your website’s loading speed on mobile devices using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix. Slow loading times can significantly hurt mobile user experience and SEO.
- Ensure mobile usability for a positive, user-friendly experience by checking if buttons, links, and forms are easy to tap with fingers. Texts should be readable and content formatted for small screens.
- Test your website across various mobile browsers eg., Chrome, Safari, or Firefox, to ensure proper functionality and display.
- Review your mobile site for SEO best practices, including optimised mobile-specific meta descriptions, proper use of headings, compressed images, and mobile-friendly URLs.
Resolving technical issues such as duplicate content
Duplicate content can dilute your SEO efforts and confuse search engines about which version of a page to rank. SEO site audit tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush can crawl your website and identify potential duplicate content.
Google Search Console (GSC) may also report instances of duplicate content under the “Coverage” section. In some cases, a manual review of your website content might be necessary.
Resolving Duplicate Content with Canonical Tags:
- Canonical Tag Implementation: When you’ve identified duplicate content, use the rel=”canonical” tag to specify the preferred version for search engine This instructs search engines to consider the canonical URL for indexing and ranking purposes.
- It’s generally good practice to include a self-referencing canonical tag on every page of your website, even if there are no duplicates.
- Set up 301 redirects, using the canonical link element to indicate the preferred version of a page or;
- Simply rewrite the content to eliminate duplication and provide unique value.
On-page SEO audit
In conducting an on-page SEO audit, you have to look into various aspects, such as content quality, keyword usage in meta tags and headings, internal and external link quality, the presence of any duplicate content, and the overall user experience. Each element can either positively or negatively impact your site’s relevance and authority from the perspective of search engines like Google.
Let’s dissect these on-page elements and provide actionable steps to help you fine-tune your website for better SEO performance.
Optimising meta tags and headings for target keywords
Before optimising your content, ensure you have a solid foundation of relevant target keywords. Conduct keyword research to identify keywords with good search volume that align with your website’s content and target audience.
Optimising Meta Tags
- Title Tag: This is the most crucial meta tag. Include your target keyword naturally within the first 60 characters. Keep it informative, concise, and compelling to encourage clicks.
- Meta Description: A well-written meta description that includes your target keyword can significantly improve click-through rates (CTR) in search results. Write a compelling description that entices users to click on your result in the SERPs. Keep it concise, ideally under 160 characters.
Optimising Headings
- H1 Tag is the main heading on your page and should ideally include your target keyword in a natural way. There should only be one H1 tag per page.
- Maintain a clear hierarchy of H2, H3, H3, and H4 (if needed), strategically incorporating relevant keywords
Reviewing and improving the internal linking structure
Internal links are the roadways that connect the content within your website, allowing users to navigate and search engines to establish an information hierarchy.
- Ensure each page is accessible through internal links and that anchor text is relevant and descriptive.
- High-value content should be linked frequently, which signals to search engines about the importance and relevance of the pages.
- Audit your site to identify opportunities to enhance internal links, particularly for pages you’re prioritising for ranking improvements.
Assessing the quality and relevance of external links
External links, or backlinks, are endorsements from other websites, and they remain among the top-ranking factors. The number of backlinks from high-authority websites and the diversity of anchor text used in these backlinks directly influence a site’s credibility and search ranking.
It’s crucial to analyse the quality and quantity of backlinks pointing to the website to assess its authority and credibility.
Additionally, examining the domain authority score of linking domains offers valuable insight into the trustworthiness of the sources linking back to the website. A higher domain authority score signifies that the link is coming from a reputable and established source, contributing positively to the website’s own authority.
Enhancing user experience through clear navigation and intuitive design
Lastly, user experience (UX) has a direct impact on SEO. Search engines prioritise sites that provide a good user experience, as indicated by metrics like time on page, bounce rate, and click-through rate.
During an on-page SEO audit, assess your site’s navigation—is it logical and easy to follow? Is your design intuitive so users can find the information they seek without frustration?
Significant UX elements include the following:
- a clear hierarchy
- accessible menus, and
- a responsive design that adjusts seamlessly to different screen sizes.
By improving UX, you not only cater to your human visitors but also to the search engine algorithms that rank your pages.
Content audit
A Content Audit is a critical component of any SEO audit checklist, as it revolves around assessing every piece of content on your website to ensure it aligns with your SEO strategy and business objectives.
The process includes evaluating the quality and relevance of your content, pinpointing gaps that might benefit from fresh, keyword-focused content, and tweaking existing pieces to harmonise with target keywords and the underlying user intent.
Relevance is as important, with each page needing to resonate with your audience’s search queries and expectations. This measure of quality and relevance impacts user engagement, which in turn signals the value your site provides to its visitors.
Identifying opportunities for creating quality content
Gaps will often emerge in content audits, highlighting the potential for new topics that haven’t been addressed on your site. These gaps offer opportunities to expand your content’s scope and capture additional organic traffic.
Conduct keyword research to uncover terms and phrases your target audience is searching for but that you may not have used in your existing content. Developing fresh content around these keywords not only fills the gaps but also helps to establish your site as an authoritative source of information.
Optimising existing content for target keywords and user intent
Optimisation goes beyond keyword insertion. It involves tuning your existing content to ensure it aligns with the keywords you are targeting and the intent behind user searches. User intent refers to the reason why someone conducts a specific search query.
Analyse your existing content and target keywords by asking these questions:
- What information are users seeking from this topic?
- Are they looking to learn (informational), compare products (commercial), or make a purchase (transactional)?
When doing keyword research, focus on the user intent you identified. Look for relevant keywords with good search volume that users might employ for informational, commercial, or transactional searches related to your content.
Ensuring proper keyword placement and density
Keywords should be integrated strategically throughout your content, including title tags, headings, and the body text —but without overdoing it.
Keyword stuffing, or the overuse of keywords, can have a detrimental effect, making the content difficult to read and potentially triggering search engine penalties. Instead, a balanced approach that considers keyword density and related terms can provide context and relevance without compromising on the natural flow and readability of your content.
Avoiding Keyword Cannibalization
In SEO, keyword cannibalisation occurs when multiple pages on your website compete against each other for the same keywords and search engine rankings. This competition weakens the overall ranking power of each individual page.
For instance, having two blog posts targeting the keyword “best-running shoes” in which both pages have similar content and with the same intent. Search engines might get confused about which page is truly the most relevant for the search query, and as a result, neither page ranks very well.
How to Find Cannibalization During an SEO Audit
There are a few ways to identify cannibalisation during an SEO audit:
- Keyword Mapping: Create a map that shows which pages target which keywords. Look for instances where multiple pages target the same or very similar keywords.
- Content Analysis: Manually review pages that are targeting the same keywords. Are they too similar? Do they both serve the same purpose for the user?
- SEO Tools: Use SEO tools to identify cannibalisation issues. These tools can crawl your website and identify pages with overlapping content or that target the same keywords.
Fixing Cannibalization
Once you’ve identified cannibalisation issues, you can address them in a few ways:
- If you have multiple pages with very similar content, consider combining them into a single, more comprehensive page.
- If the pages have some unique value but target similar keywords, rewrite the content to focus on different aspects of the topic.
- Use internal linking strategically to point users and link juice to the most relevant page for a particular keyword.
- Ensure each page has unique meta tags and title tags that accurately reflect the content and target keywordpen_spark
Analysing SEO performance and metrics
SEO audits aren’t just about combing through your website’s technical and content makeup. They’re also about measuring the effectiveness of your optimisations.
Tracking the right metrics allows for data-driven decisions that can elevate a website’s search engine rankings and enhance visibility among the target audience.
Monitoring organic traffic and rankings
Monitoring your site’s organic traffic is a cornerstone of SEO analysis. It involves tracking the number of visitors that come to your site through non-paid search results. By reviewing organic traffic, you get a clear view of your SEO’s health—a steady or increasing flow indicates successful optimisations.
Similarly, keeping an eye on your search rankings for targeted keywords offers insights into how your content resonates with both search engines and users.
Utilise tools like Google Search Console to analyse performance data, such as which pages receive the most clicks and how they rank for specific queries.
Tracking click-through rates (CTR) and conversions
CTR indicates how successful your website listing is in search engine results pages at grabbing attention and enticing users to click through. This metric helps to evaluate the effectiveness of your title tags and meta descriptions, which are critical elements that entice users to visit your site.
Meanwhile, tracking conversions is vital to understanding how those clicks translate into actions, whether it be a sale, a subscription, or another goal.
By analysing both CTR and conversions, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of your SEO performance. A high CTR might indicate successful lead generation from search, but a low conversion rate suggests room for improvement in converting those leads into customers.
Analysing bounce rates and user engagement metrics
Bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who land on a single page of your website and leave without visiting any other pages.
Engagement metrics like session duration and pages per session provide deeper insights into how visitors interact with your site.
Analysing Bounce Rate and User Engagement
- High Bounce Rate & Low Engagement: This combination suggests significant issues with user experience or content relevance. Users are likely arriving, finding the page doesn’t meet their needs, and leaving quickly.
- Low Bounce Rate & High Engagement: This is a positive sign, indicating users are finding your content engaging and navigating deeper into your website.
Analysing both bounce rate and user engagement metrics can help you gain a deeper understanding of how users interact with your website and identify areas for improvement.
Utilising Google Analytics and Google Search Console for insights
Google Analytics and Google Search Console are your go-to tools for gathering rich insights into your website’s SEO performance.
Google Analytics offers an in-depth look at user behaviour, traffic sources, and conversion data, while Google Search Console focuses on how your site appears in search results, with information on indexing status, mobile usability, and more.
Use Google Analytics Acquisition Reports to see how users are finding your website. This will tell you the percentage of traffic coming from organic search compared to other channels like social media or direct traffic.
Within Google Search Console, the “Search Results” section provides insights into how your website appears in (SERPs). You can see:
- Keywords: The keywords users are searching for that trigger your website’s appearance in the SERPs.
- Impressions: The number of times your website appeared in search results for those keywords.
- Clicks: The number of times users clicked on your website from the SERPs.
- Click-through Rate (CTR): This metric (clicks divided by impressions) tells you how successful your website listing is in grabbing attention and enticing clicks.
Combining Insights for Actionable Strategies
- Use Google Search Console to identify keywords with high impressions and CTR. Then, delve into Google Analytics to see if those keywords are driving valuable traffic (high time spent on page, low bounce rate) and conversions.
- For keywords with high impressions but low CTR, analyse the landing pages in Google Analytic Are they user-friendly? Does the content address the search intent? Make data-driven improvements to boost conversions.
- Set up conversion goals in Google Analytics to track how organic search traffic contributes to your overall business objectives (e.g., purchases and signups).
Remember, the key to a successful SEO auditSet up conversion goals in Google Analytics to track how organic search traffic contributes to your overall business objectives (e.g., purchases and signups). is the continuous measurement and analysis of pertinent metrics that align closely with your business objectives. Regularly auditing these metrics will ensure you’re on the right track towards improving your site’s SEO and achieving sustainable growth in organic traffic and conversions.
Conclusion
An SEO audit is a comprehensive analysis of your website’s health and search engine optimisation (SEO) effectiveness. It’s not a one-time fix but an ongoing process that ensures your website remains competitive and ranks well in search results.
Remember, a successful SEO audit hinges on setting clear goals, gathering relevant data, and taking action based on your findings. By continuously monitoring and analysing key metrics, you can make data-driven decisions that elevate your website’s ranking and achieve long-term SEO success.